High carbon steel refers to carbon steel with W (C) higher than 0.6%, which has a greater tendency to harden than medium carbon steel and forms high carbon martensite, which is more sensitive to the formation of cold cracks.At the same time, the martensite structure formed in the welding heat affected zone, hard and brittle performance, resulting in the joint plasticity and toughness greatly reduced, so the weldability of high carbon steel is quite poor, special welding process must be taken to ensure the joint performance.
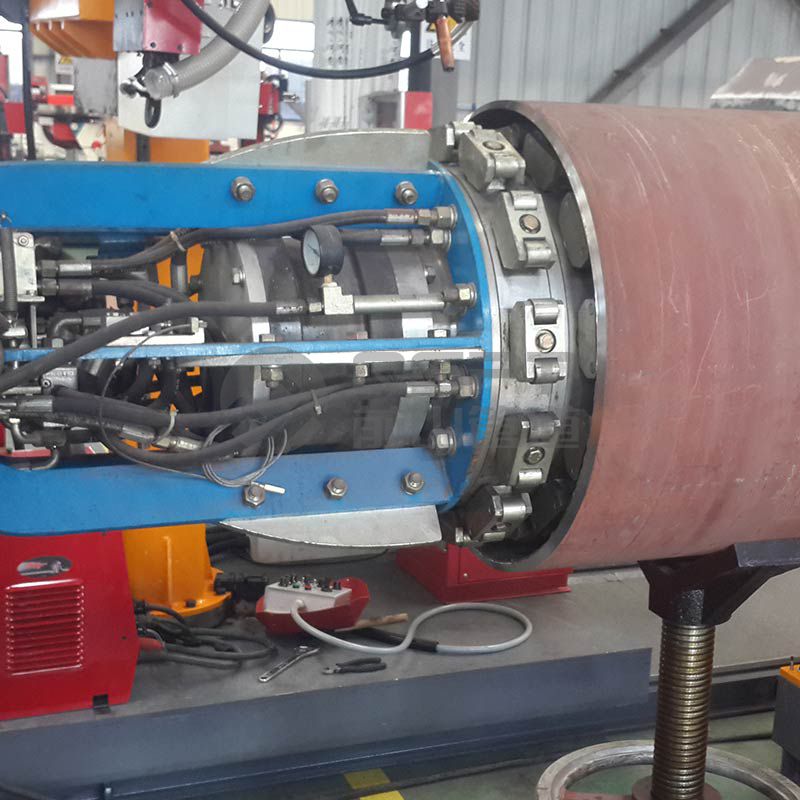
In heavy machinery manufacturing, there are also welding problems of high carbon steel parts. When making the welding process of high carbon steel welding parts, all possible welding defects should be analyzed comprehensively and corresponding welding process measures should be taken.

1.1 Welding Method
High carbon steel is mainly used for high hardness and high wear resistance structure, so the main welding methods are electrode arc welding, brazing and submerged arc welding.
1.2 Welding Materials
High carbon steel welding generally does not require equal strength of joint and base metal. Electrode arc welding generally selects the low hydrogen electrode with strong sulfur removal ability, low hydrogen content of metal diffusion and good toughness.In the requirement of weld metal and base metal strength, should choose the corresponding level of low hydrogen electrode; When the strength of weld metal and base metal is not required, the low hydrogen electrode with a strength level lower than the base metal should be selected. Remember that the electrode with a strength level higher than the base metal can not be selected.If the base metal is not allowed to preheat during welding, in order to prevent cold cracks in the heat affected zone, the austenitic stainless steel electrode can be used to obtain good plasticity and strong crack-resistant austenite structure.
1.3 Groove preparation
In order to limit the mass fraction of carbon in the weld metal, the fusion ratio should be reduced, so u-shaped or V-shaped groove is generally used in welding, and pay attention to clean the oil and rust in the groove and the range of 20mm on both sides of the groove.
1.4 preheating
When welding with structural steel electrode, preheating must be carried out before welding, and the preheating temperature should be controlled between 250℃ and 350℃.
1.5 Interlayer processing
Multi-layer multi-pass welding, the first welding using small diameter electrode, small current welding. Generally, the workpiece is placed in semi-vertical welding or the use of transverse swing welding rod, so that the whole base metal heat affected area is heated in a short time, in order to obtain preheating and insulation effect.
1.6 Post-welding heat treatment
Immediately after welding, the workpiece is put into the heating furnace and kept at 650℃ for stress relief annealing [3].

 2021-11-12
2021-11-12