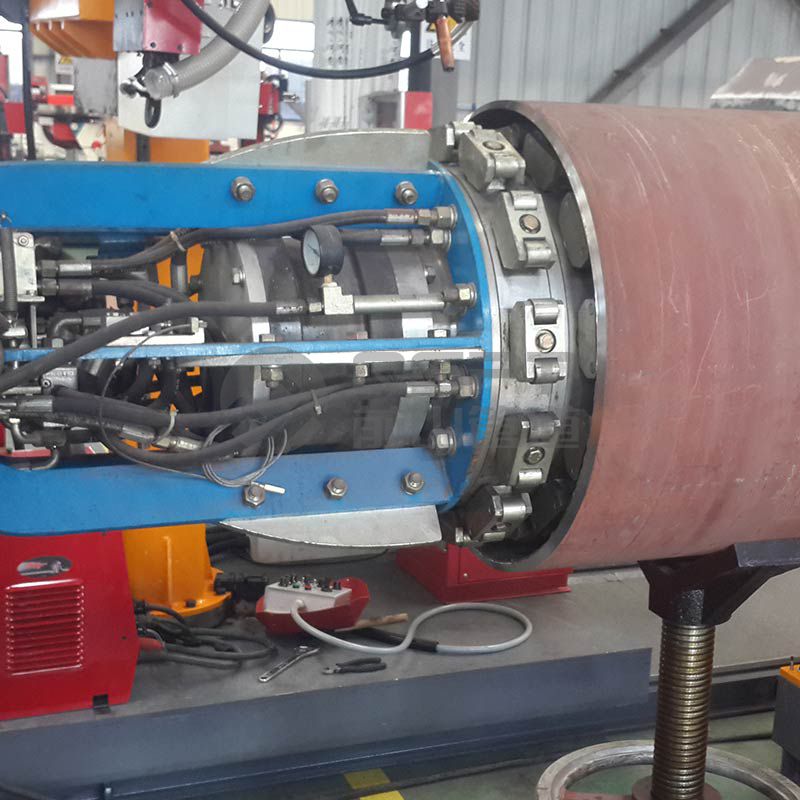
1.1 Welding of thick plate and thin plate
1, when welding steel workpiece with GMAW and Flux cored wire gas shielded welding (FCAW), if the plate thickness of the workpiece exceeds the maximum welding current that can be reached by the welder, how will it be handled?
The solution is to preheat the metal before welding. Propane, gas or acetylene torch is used to preheat the welding area of the workpiece. The preheating temperature is 150 ~ 260℃, and then welding is carried out. The purpose of preheating the metal in the welding area is to prevent the weld area from cooling too fast, so that the weld does not crack or not fuse.
2. If it is necessary to weld a thin metal cover to a thicker steel pipe using GAS shielded gas welding or flux cored wire welding, two situations may occur if the welding current cannot be properly adjusted during welding:
First, in order to prevent the thin metal from burning through and reduce the welding current, the thin metal cover can not be welded to the thick steel pipe; Second, the welding current is too large to burn through the thin metal cover. How should this be handled?
There are two main solutions.
① Adjust the welding current to avoid burning through the thin metal cover, and use the torch to preheat the thick steel pipe, and then use the thin plate welding process to weld the two-metal structure.
② Adjust the welding current to be suitable for the welding of thick steel pipe. When welding, keep the welding arc residence time on the thick steel tube at 90% and reduce the residence time on the thin metal cover. It should be noted that good welding joints can be obtained only when this technique is mastered.

3. When welding a thin-walled round pipe or rectangular thin-walled pipe to a thick plate, the welding rod is easy to burn through the thin-walled pipe part. In addition to the above two solutions, are there any other solutions?
B: Yes, mainly using a radiator rod during welding. If a solid round rod is inserted into a thin-walled round tube, or a solid rectangular rod is inserted into a rectangular fitting, the solid rod will remove heat from the thin-walled workpiece and prevent it from burning through. In general, solid round or rectangular bars are tightly installed in most hollow or rectangular pipe materials supplied. When welding, care should be taken to keep the weld away from the end of the pipe, the end of the pipe is the most vulnerable area to burn through. Use built-in heat dissipation rod to avoid burning through.
4, when it is necessary to weld galvanized or chromium-containing material with another part, how to operate?
The best method is to file or polish the area around the weld before welding, because galvanized or chromium-containing metal plates not only contaminate and weaken the weld, but also release toxic gases during welding.

 2022-04-18
2022-04-18