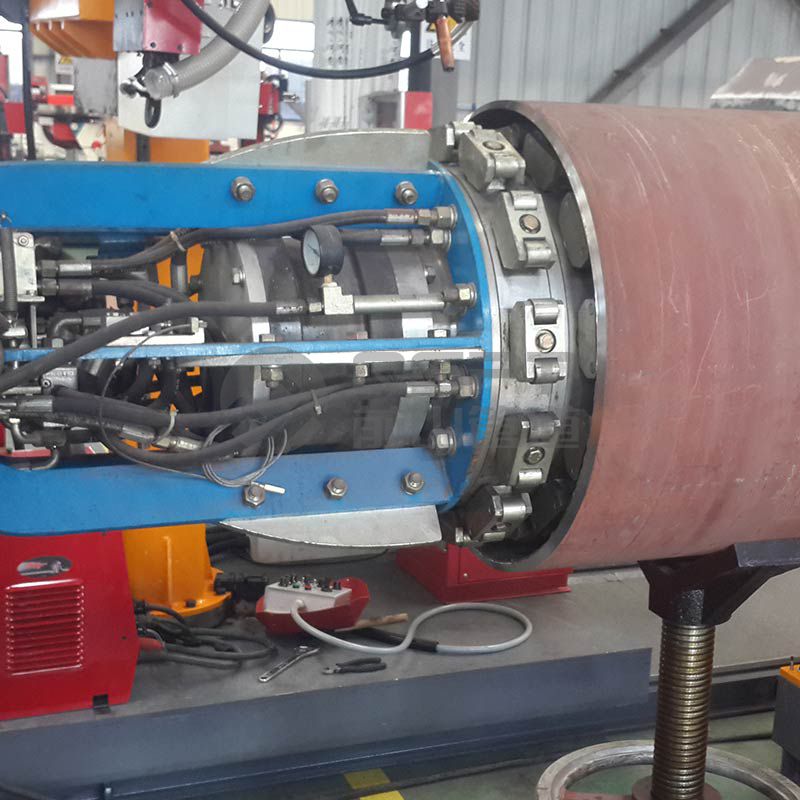
In the welding process, the welding metal due to heat input and transmission, and undergo heating, melting (or to achieve thermoplastic state) and subsequent solidification and continuous cooling process, known as the welding heat process.
The welding thermal process runs through the whole welding process and becomes one of the main factors affecting and determining the welding quality and welding productivity through the following aspects:
1) The size and distribution of heat applied to the metal determine the shape and size of the molten pool.
2) The degree of metallurgical reaction of welding pool is closely related to the effect of heat and the length of molten pool existence time.

3) The changes of welding heating and cooling parameters affect the solidification and phase transformation of molten pool metal and the transformation of metal microstructure in the heat affected zone, so the microstructure and properties of the weld and the heat affected zone are also related to the effect of heat.
4) Due to the uneven heating and cooling of each part of welding, uneven stress state is caused, resulting in different degrees of stress deformation and strain.
5) Under the action of welding heat, various forms of cracks and other metallurgical defects may occur due to the joint influence of metallurgy, stress factors and the microstructure of the metal being welded.
6) The welding input heat and its efficiency determine the melting speed of base metal and electrode (wire), thus affecting the welding productivity.

 2022-05-06
2022-05-06